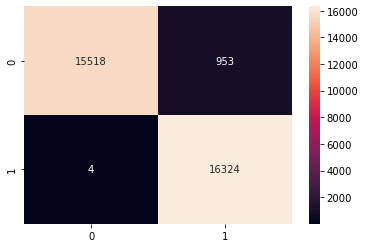
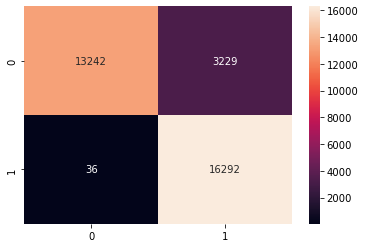
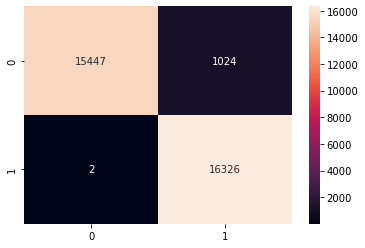
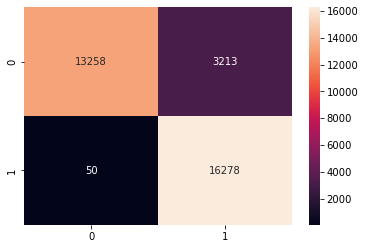
Model 1 Decision Trees
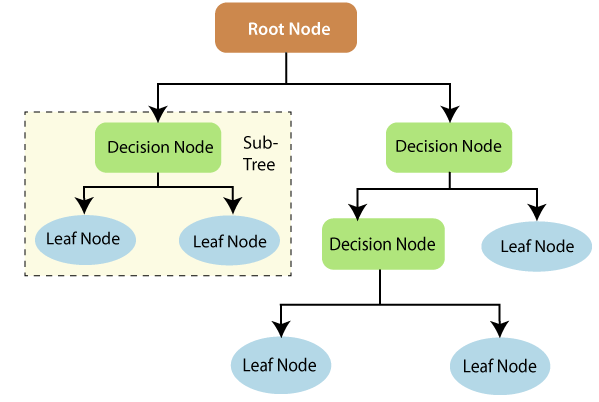
Decision trees are flowchart tree like structures where a system uses a series of questions to assign a classification. We ended up using this model for our final product.
- Accuracy: 97.08%
- Precision: 94.48%
- Recall: 99.97%
- F1: 97.15%